SSID (Service Set Identifier) is a unique name used to identify a wireless network. It is essentially the name of a Wi-Fi network that devices can see and connect to.
Example:
- If you name your home Wi-Fi network "Home_Network," that name would be the SSID. When you search for available networks, "Home_Network" would appear in the list.
Configuration for SSID:
- Go to Profile, select Wlan.
- In the Wlan section, click on the +Create Wlan button to start the process of creating a new Wlan.

Name: Enter a descriptive name for the interface.(e.g., Ray_Wlan)
Description (optional): You can add a description to explain the purpose of the interface.
- When you click to configure the Wlan, you'll be directed to the Definitions Tab.
This tab gives you two main options for Wlan configuration:
Option 1: Captive Portal
Option 2: Open/Password/Enterprise
- Choose option (Open/ Password/ Enterprise).

- Enter the SSID name (e.g., "Open_Network" or "Guest_Wifi") on highlighted part.
- Select Radios (2.4GHz, 5GHz, 2.4 & 5 GHz).

1. Open SSID (Service Set Identifier) Without Any Authentication:
- In the Security Tab, select the None option if you want to create an Open Wlan without any password.
Note:
The SSID name will be visible to anyone looking for available wireless networks, so choose a name that identifies your network clearly.

This guide should help you create an Open Wlan without any password, providing public access to the network.
Here’s a brief overview of common encryption methods used for Encryption in networking:
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2):
The most widely used encryption method for Wi-Fi networks.
Uses AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for stronger encryption.
- WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3):
The latest Wi-Fi security standard, offering improved security features.
Provides better protection against brute-force attacks, stronger encryption, and enhanced privacy.
Uses 192-bit security for enterprise networks and forward secrecy.
- WPAx:
A general term for WPA (which includes WPA2 and WPA3). It refers to both WPA2 and WPA3 standards collectively.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
This is an outdated wireless encryption protocol designed to provide a basic level of security for Wi-Fi networks. It uses 64-bit or 128-bit encryption keys, but its security is weak by modern standards, as it is vulnerable to attacks like key cracking.
Notes:
WPAx is Only Applicable for Password Authentication.
WEP has been largely replaced by more secure protocols like WPA and WPA2.
2. Password Authenticated SSID:
When you choose password authentication, it allows you to select the encryption method, as shown in the picture below.

- For Security Mode, select Password Authentication & In the next tab or field, enter the desired password (e.g., "Password@123").
Note:
Make sure to choose a strong password that is difficult to guess and meets the required character length (usually 8 characters or more).

3. Enterprise Authentication:
- Enterprise authentication refers to a secure method of verifying the identity of users or devices within a business or organizational network. It typically involves more robust security measures than consumer-level authentication, using protocol RADIUS.
For Enterprise Authentication configuration, you need to First configure RADIUS Profile.
when you choose Enterprise Authentication, it allows you to select Encryption method as shown in picture.

- For Security Mode, select Enterprise Authentication & In the next tab or field, Select RADIUS Profile.

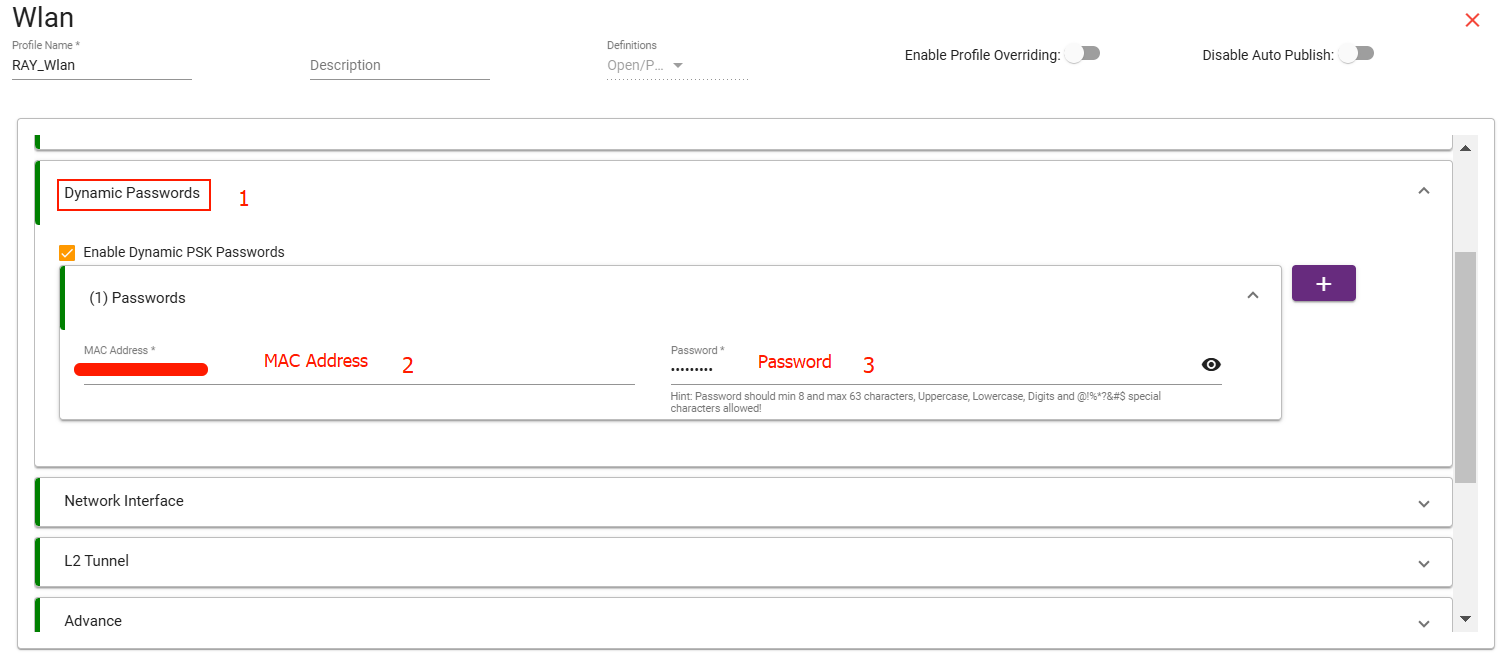
4. Dynamic Password:
In Dynamic Password Authentication, pre-authenticate the password for a specific MAC address.
- Select the 'Dynamic Password' option from the list, which will pop out a tab called 'Dynamic Passwords.

- Click on 'Dynamic Password' and Enable Dynamic PSK Passwords.
- From the drop-down menu, add The MAC address and Password. (Hint: The password should be at least 8 characters and no more than 63 characters, containing uppercase, lowercase, digits, and special characters like @!%*?&#$.)
Note:
This is suitable for those who want to assign a specific device to access the internet.
Select Network Interface
- In the Network Interfaces section, you will see the LAN and WAN interfaces you’ve previously created.
- Choose the interface for LAN and WAN from the available list for Gateway, Bridge + firewall, Bridge no firewall.


